What is Continuous Flow Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the quest for efficiency, quality, and speed has led to the adoption of various methodologies aimed at enhancing productivity and reducing costs...
By AMREP | Posted on July 24, 2024

ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It's a type of software that companies use to manage day-to-day business activities such as accounting, procurement, project management, risk management and compliance, and supply chain operations. In the context of manufacturing, ERP systems are pivotal, integrating various functions across the business to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and promote a holistic view of operations from production to delivery. Here we look at ERPs in manufacturing, reviewing its functionalities, benefits, challenges, and the future outlook.
ERP systems are the backbone of modern manufacturing operations as they provide a centralized platform to manage and analyze data from various business processes. By consolidating information from different sources, ERP systems enable manufacturers to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and respond dynamically to market demands.
In manufacturing, ERP systems play a critical role in optimizing operations, enhancing efficiency, and driving productivity. Here are the core functionalities of ERP in manufacturing:
Read More: A3 Process: A Structured Problem-Solving Approach
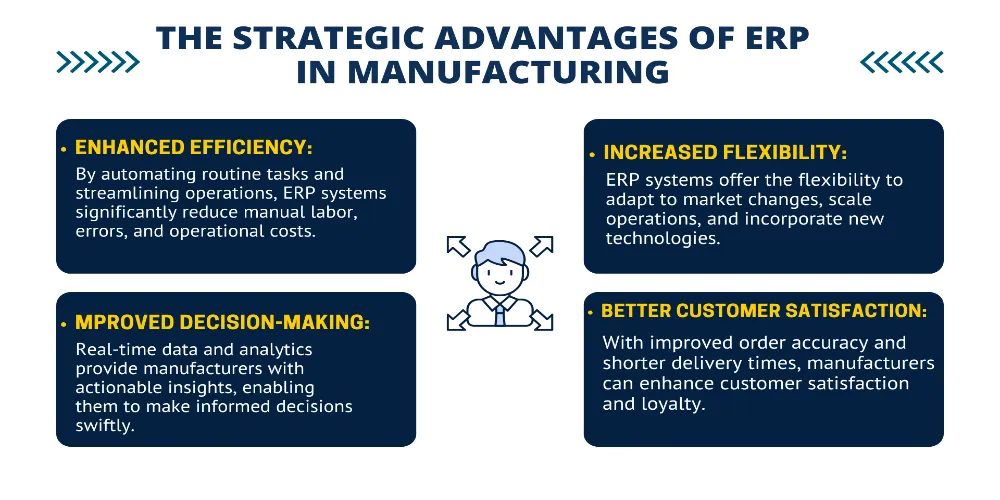
Implementing an ERP system can transform the manufacturing landscape of a company, offering several strategic advantages.
While ERP systems offer substantial benefits, their implementation is not without challenges.
The future of ERP in manufacturing is dynamic and promising, driven by technological advancements and evolving business needs.Here are some new developments:
Despite the challenges associated with implementation and adoption, the rewards make ERP an essential investment for manufacturers aiming to thrive in an increasingly competitive and complex industry landscape. The integration of ERP with cutting-edge technologies promises not only to streamline operations but also to open new avenues for innovation, customization, and growth in the manufacturing sector. Embracing ERP is not just about keeping pace with technological advancements; it's about setting the stage for sustained success in a rapidly evolving global market.
At AMREP, we’ve designed our own ERP systems for our human resources management, accounting, and quality management work. We also build customized systems for our clients to handle their inspection report data - this is particularly useful for clients who have large shipments and inspection volumes. With our system, they are easily able to access our inspection reports and product defect data.
The Effectiveness of Enterprise Resource Planning- ERP Implementation in Manufacturing Industry.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/318445385_THE_EFFECTIVENESS_OF_ENTERPRISE_RESOURCE_PLANNING-_ERP_IMPLEMENTATION_IN_MANUFACTURING_INDUSTRYRole of ERP Software in the Manufacturing Industry.
https://www.globaltrademag.com/role-of-erp-software-in-manufacturing-industry/Enterprise resource planning.
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


23 - July 2024
23
July
2024
In manufacturing, the quest for efficiency, quality, and speed has led to the adoption of various methodologies aimed at enhancing productivity and reducing costs...

18 - July 2024
18
July
2024
Return Merchandise Authorization, or RMA for short, plays a pivotal role in both manufacturing and retail worlds. It connects two critical concepts...
12 - July 2024
12
July
2024
Traceability in manufacturing refers to the ability to track and trace every aspect of the production and distribution process...
