Initial Production Inspection (IPI)
Quality control is not just about checking the finished product; it's about taking the right steps from ...
By AMREP | Posted on March 05, 2025

Quality inspectors are employed across all manufacturing industries to carefully examine finished products for defects such as scratches, dents, and imperfections in seams. These professionals inspect a wide variety of products, including clothing, automobiles, and toys. In manufacturing environments, these roles may also be referred to as materials inspectors or mechanical inspectors. Continue reading to discover the earning potential, key skills, and daily responsibilities of a quality inspector.
Quality Control Inspectors are responsible for ensuring that products or services meet the required standards of quality. They perform tasks like:
Must See: QC Tests and Checks
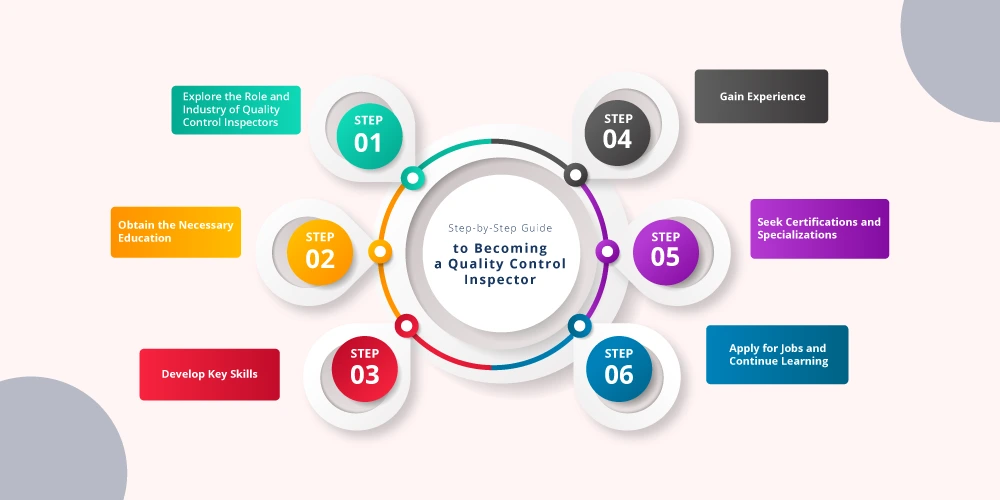
Before exploring the details of becoming a Quality Control Inspector, it's essential to first familiarize yourself with the industries where these professionals are needed. These industries may include:
Gaining an understanding of the industries that employ quality control professionals will allow you to shape your career path more effectively and identify the key skills and certifications that are most valuable.
A formal degree is not always required to become a quality control inspector, but it certainly helps in advancing your career and broadening your job opportunities. Here are some educational options:
Many employers also offer on-the-job training, especially for entry-level positions, to help you learn the ins and outs of specific industry standards.
Quality Control Inspectors need a combination of technical and soft skills to perform their jobs effectively. These skills include:
Hands-on experience is one of the most effective ways to build your skills and advance in the field. Here’s how you can gain experience:
Experience will help you refine your technical skills, become comfortable with inspection equipment, and get accustomed to common industry challenges.
While certifications aren’t always required, they do improve your career prospects. The Certified Quality Inspector (CQI) certification, provided by the American Society for Quality (ASQ), is one of the most recognized certifications for quality control inspectors. Additionally, many industries require specific certifications or compliance with standards such as:
These certifications demonstrate your competence, improve your chances of promotion, and give you a competitive edge in the job market.
Once you have the required education, experience, and certifications, it's time to apply for positions. Job boards, recruitment agencies, and company websites are great places to start. Many job titles for quality control inspectors include:
Even after securing a job, the best inspectors continue learning and adapting to new technologies, regulations, and industry standards. Attending conferences, participating in workshops, and joining professional associations can further advance your career.
Read More: Quality Control in Automotive Industry
Quality control inspectors use a variety of specialized equipment to ensure products meet specified standards. The types of equipment they use depend on the industry and the specific inspection needs. Here are some common tools:
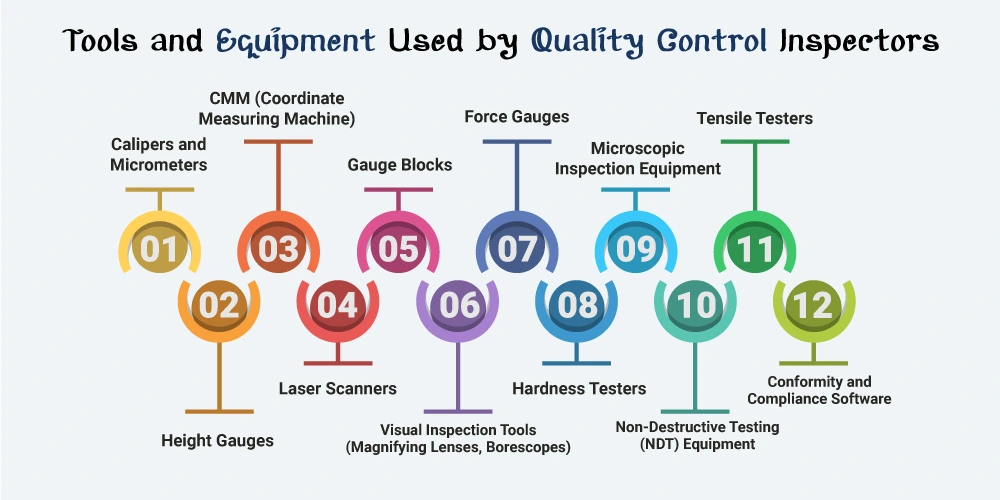
Used for measuring dimensions with high precision, calipers and micrometers help inspectors check the size, thickness, and diameter of products or components.
These are used to measure the height of objects and components, ensuring they meet the required specifications.
A CMM is used to measure the physical geometrical characteristics of an object. The machine can be operated manually or controlled via computer software to gather precise data on 3D dimensions.
These devices are used for 3D scanning and mapping the surfaces of parts or products, providing highly accurate measurements and identifying defects.
Used to calibrate measuring equipment and check the accuracy of tools, gauge blocks provide a standard reference for measurements.
If defects are found, they’re categorized by severity—whether minor, major, or critical— and documented in a detailed report. This allows you to make informed decisions on whether or not to proceed with mass production.
Magnifying tools and borescopes help inspectors look for visual defects or irregularities that may be too small to see with the naked eye.
These measure the force required to move or compress an object and can be used to check the strength and durability of products.
Hardness testers assess the hardness of materials, ensuring they meet required strength levels, commonly used in materials like metals or plastics.
Inspectors sometimes use microscopes or other magnifying tools for examining the surface or internal structure of parts, especially in electronics or precision engineering.
For inspections that don’t damage the product, NDT equipment like ultrasonic testers, X-ray machines, and dye penetrant kits are used to detect cracks or flaws inside materials.
These are used to measure the strength of materials by testing how much force a material can withstand before breaking or deforming.
In some cases, inspectors use specialized software to compare product measurements against standards and specifications, ensuring compliance with regulatory or quality guidelines.
Certifications are a great way to enhance your credibility and showcase your expertise as a Quality Control Inspector. Here are some key certifications that can help boost your career:
Offered by the American Society for Quality (ASQ), the CQI certification demonstrates proficiency in inspection techniques, statistical process control, and measurement methods. It's ideal for those focused on quality inspection.
The Certified Welding Inspector (CWI), provided by the American Welding Society (AWS), is for those in welding inspection. It covers welding codes, processes, and inspection techniques, making it vital for industries involving welding.
The CMI certification, also from ASQ, focuses on mechanical inspection techniques for professionals in industries like manufacturing and automotive. It covers mechanical systems, components, and quality practices.
The CQT certification (offered by ASQ) is for professionals in quality control roles, including inspection. It covers quality concepts, measurement, and statistical techniques to improve overall quality management.
NDT certifications, from organizations like the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT), specialize in testing methods such as ultrasonic or radiographic testing. These certifications are essential for industries relying on nondestructive methods to assess product integrity.
The CQA certification from ASQ focuses on auditing quality management systems. It’s beneficial for professionals interested in both inspection and auditing, covering topics like quality system evaluation and compliance.
This certification demonstrates expertise in auditing quality management systems against ISO 9001:2015 standards. It's ideal for those assessing compliance and improving quality management processes within organizations.
The career outlook for Quality Control Inspectors is generally positive, especially in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and pharmaceuticals, where the demand for high-quality products is constant. As you gain experience and certifications, you may have the opportunity to move into supervisory roles or specialized areas, such as:
As of May 2023, the median annual salary for quality control inspectors was $45,850. The median wage represents the middle point, where half of workers in this field earn more and half earn less. The lowest 10 percent of workers made less than $31,950, while the highest 10 percent earned over $72,210.
The median annual wages for quality control inspectors across various industries in May 2023 were:
Most quality control inspectors work full-time, but some may be required to work evening, night, or weekend shifts, depending on seniority or production needs. Overtime work may also be necessary to meet tight production deadlines.
A quality control inspector is a rewarding career path that requires a keen eye for detail, a strong understanding of industry standards, and the right certifications.
At AMREP, as manufacturing experts, we are committed to fostering talent in the quality control field and providing opportunities for growth and development. If you're ready to take the next step in your career, explore how AMREP can support you in achieving your professional goals.
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


28 - February 2025
28
February
2025
Quality control is not just about checking the finished product; it's about taking the right steps from ...

27 - February 2025
27
February
2025
Quality isn’t a choice; it’s a commitment that begins the moment production starts. PwC’s Global Manufacturing Report suggests that companies ...

19 - February 2025
19
February
2025
Companies rely on QC professionals to detect defects, prevent errors, and improve processes. But what skills are necessary for success in this field? To excel ...
