Quality Control in Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, product quality is an important issue as it is linked to safety and human life. And the ...
By AMREP | Posted on February 13, 2025
Quality Control (QC) tests and checks ensure that every product leaving the production line is reliable, functional, and defect-free. QC techniques help manufacturers identify issues early, prevent costly mistakes, and maintain customer satisfaction. These systematic processes not only improve product consistency but also streamline production workflows.
In the following sections, we’ll dive deeper into the different types of QC tests and checks that businesses use to maintain high standards and deliver top-quality products.

Quality Control (QC) Testing refers to the process of evaluating and inspecting products or services to ensure they meet predefined standards of quality. The primary goal of QC testing is to identify any defects, inconsistencies, or potential issues before a product is released to the market or a service is provided to customers. QC testing plays a crucial role in maintaining high-quality standards and customer satisfaction.
Quality Control (QC) tests are critical to ensuring that products meet the desired standards. There are several types of QC tests conducted at different stages of production to verify a product's quality and functionality. Here are the most common types of QC tests:

The most basic form of QC is visual inspection. Inspectors check for visible defects, damages, or inconsistencies. This test is often the first step in identifying issues.
This test checks if a product works as intended. It ensures the functionality of each component. For example, in electronics, this could mean testing buttons, displays, or ports.
Dimensional checks verify that the size and shape of a product match the specifications. Measuring tools like calipers or micrometers are used to ensure precision.
Performance tests measure how well a product functions under specific conditions. For example, a car might undergo high-speed tests or temperature tests to check its performance in various environments.
Stress tests push products beyond their normal limits to see how they perform. This is particularly important in industries like software, construction, or manufacturing, where reliability is critical.
Material tests check the properties of raw materials. These tests ensure that materials used in production meet safety and durability standards.
Packaging must protect products during transportation. Packaging tests ensure that the product can survive handling, shipping, and storage without damage.
Read More: Quality Control in Automotive Industry
QC tests and checks are essential to ensure that products meet the required standards of quality, safety, and functionality.
QC tests help identify defects that could make a product unsafe. In industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and automotive, safety is paramount.
Products that meet high standards of quality are less likely to break or cause issues. This results in happy customers and positive reviews.
Identifying defects early in the production process prevents costly recalls or repairs. QC checks save money in the long run by preventing waste.
Many industries have strict regulations. QC tests ensure that products comply with these rules, avoiding fines or legal trouble.
Consistently delivering high-quality products builds trust with consumers. A good reputation leads to brand loyalty and growth.
Think about a product that’s let you down. Whether it’s a broken device, a damaged item, or something that didn’t live up to its promises, you likely wouldn’t want to buy from that brand again. Quality control testing is what separates great brands from the rest—it builds customer loyalty by ensuring that products meet or exceed expectations.
For instance, Apple is known for its high-quality, reliable products, which are consistently tested through various QC measures. From the dimensional checks on their device components to the performance testing of the iPhone’s battery life, Apple’s QC process ensures that every product delivers an exceptional experience.
Must See: Quality Control Methods
Quality Control (QC) testing is essential for maintaining high standards of product quality, but it comes with a variety of challenges that can complicate the process. These challenges can affect the efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of QC efforts. Below are some of the key challenges faced by QC testing teams:
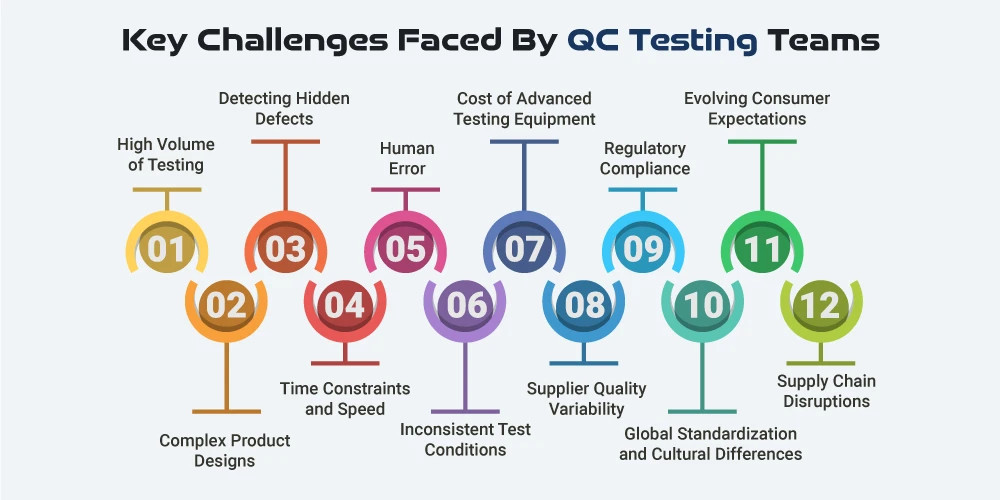
As production scales up, the volume of products that need to be tested also increases. High-volume testing can lead to logistical challenges such as time constraints, resource limitations, and increased labor costs. Maintaining consistent and thorough testing across a large number of products, without missing critical defects, can be difficult to manage.
In industries such as electronics, automotive manufacturing, and aerospace, products are becoming increasingly complex. Products with intricate components and systems require more detailed and advanced testing. QC testers may need specialized equipment and techniques to ensure that all parts of a product perform as expected. Managing these complexities within the testing process can be overwhelming, especially when unexpected design changes occur.
Certain defects are not visible to the naked eye and can only be detected through advanced techniques like X-ray imaging, ultrasonic testing, or stress tests. Hidden flaws such as microfractures in materials, subtle circuit defects, or small manufacturing errors can easily go unnoticed during traditional visual inspections or basic testing. The challenge lies in using the right tools to identify hidden defects without compromising efficiency.
In fast-paced manufacturing environments, speed is often a priority. The pressure to meet deadlines and reduce time-to-market can result in rushed QC testing. Insufficient testing time may lead to incomplete inspections, which in turn can allow defective products to reach the market. Balancing the need for thorough testing with the demand for quick turnaround can be a difficult task for QC teams.
Despite advancements in automation and technology, human error is still a significant challenge in QC testing. Mistakes can occur during the testing process, whether it's from misinterpreting results, overlooking a defect, or incorrect handling of testing equipment. This can lead to faulty products being approved and shipped to consumers, potentially damaging the company’s reputation.
Quality tests must be conducted under consistent and controlled conditions, but in real-world manufacturing, test environments can vary. Factors like temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, or equipment wear-and-tear can impact test results. Variability in conditions can lead to inaccurate test outcomes, making it difficult to assess the true performance and reliability of a product.
Advanced QC testing often requires specialized equipment, such as high-resolution microscopes, material testing machines, or automated visual inspection systems. The cost of purchasing, maintaining, and calibrating this equipment can be prohibitive, especially for smaller businesses. This makes it difficult to implement and sustain high-quality testing without investing heavily in advanced technology.
In many industries, manufacturers depend on external suppliers for raw materials and components. Supplier variability in material quality or component production can lead to inconsistency in the final product. Even with rigorous QC testing on-site, defects stemming from raw materials or outsourced components can still impact the overall quality of the finished product. This creates the challenge of ensuring that both internal and external sources meet the same stringent quality standards.
QC testing in industries like pharmaceuticals, food production, and medical devices must comply with strict regulations set by governing bodies (e.g., the FDA, ISO standards). Meeting these regulatory requirements while ensuring that testing is both accurate and efficient can be difficult. Compliance often involves extensive documentation and audits, which can be time-consuming and challenging to maintain consistently across multiple production cycles.
In global markets, manufacturers often need to meet a variety of international standards for different regions or countries. Testing protocols that are effective in one location may need to be adjusted to comply with local regulations or market expectations. Additionally, cultural differences in production practices or product preferences can further complicate QC efforts, especially in multinational companies.
As consumers become more demanding, product expectations continue to rise. QC teams are under increasing pressure to ensure that products not only function perfectly but also have superior aesthetics, design quality, and user experience. The rapid pace of technological innovation also means that QC teams must adapt to new testing criteria, methods, and standards in real-time.
Supply chain disruptions, like delays in receiving raw materials, transportation bottlenecks, or changes in suppliers, can significantly affect the QC process. Disruptions can lead to incomplete batches, incomplete tests, or extended delays in obtaining materials for testing, all of which impact the ability to maintain consistent quality control over production.
At AMREP Inspect, we are committed to delivering comprehensive QC solutions tailored to your specific needs, ensuring every product meets the rigorous standards required in today’s competitive market. Our Quality Management System (QMS) is designed to maintain consistency and control throughout every phase of production. By partnering with us, you can trust that your products are in expert hands, safeguarding your brand’s reputation and customer satisfaction at every stage of production.
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


22 - January 2025
22
January
2025
In the automotive industry, product quality is an important issue as it is linked to safety and human life. And the ...

07 - January 2025
07
January
2025
The emphasis on customer satisfaction and continuous quality improvement is central to both quality assurance and quality control. Quality assurance ...

20 - December 2024
20
December
2024
Quality is a key differentiator for success, and organizations must adopt strategies that drive continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Total Quality Management...
