What is a Layered Process Audit?
Layered Process Audit is a quality tool designed specifically for manufacturing management. It is meant for auditing organizational processes ...
By AMREP | Posted on February 02, 2024

Continuous improvement and Lean systems are related concepts that aim to enhance the efficiency, quality, and value of products and services. Continuous improvement is the ongoing process of analyzing performance, identifying opportunities, and making incremental changes to processes, products, and operations. Lean systems are a set of management principles that focus on eliminating waste and maximizing value by streamlining workflows and empowering employees.
Both concepts are essential in manufacturing. Many original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) require their suppliers to continuously implement improvements to improve production outcomes, enhance yields, and reduce costs. Some OEMs take an active role in developing their suppliers’ capabilities in these areas and sometimes deploy third party supplier development specialists, such as AMREP, to train the supplier.
The origins and development of Lean continuous improvement can be traced back to the Toyota Production System (TPS), which was pioneered by Toyota in the 1950s. TPS was a revolutionary approach to manufacturing that sought to eliminate waste, enhance efficiency, and deliver maximum value to customers. It introduced concepts like just-in-time production, automation, and Kaizen which means continuous improvement in Japanese. TPS was influenced by the earlier work of Fredrick Taylor, Henry Ford, Shigeo Shingo, and Taiichi Ohno, among others. Over time, TPS became widely adopted by companies worldwide, transforming manufacturing practices and setting the stage for Lean to become a globally recognized and influential methodology in various industries.
The key principles and goals of Lean continuous improvement are based on the idea of respect for people and the pursuit of perfection. The five principles of Lean are:
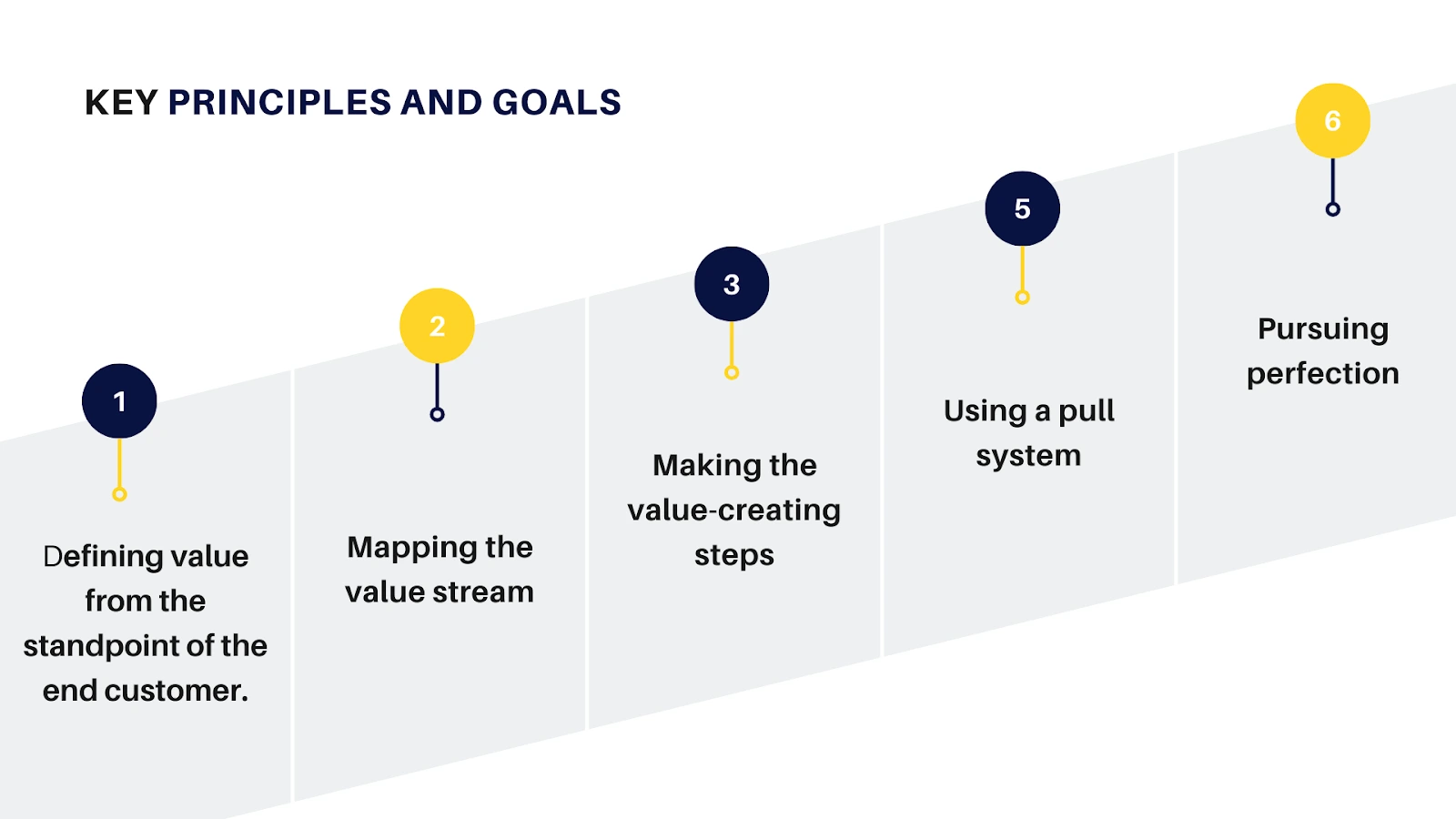
The goals of Lean continuous improvement are to reduce costs, minimize lead times, enhance product quality, and respond more effectively to customer demands.
Must Read:5 Phases Of Six Sigma
Continuous improvement is a key principle of Lean methodology. It aims to make every process in your company better by adding more value for your customer and eliminating more waste.
Waste is anything that does not contribute to your customer’s satisfaction. Lean identifies three main types of waste: Muda, Mura, and Muri.
Lean Continuous Improvement is a never-ending process of making your products, services, or processes better by adding more value for your customer and removing more waste. You can use a six-step method to plan, sequence, and carry out improvement efforts in your organization.
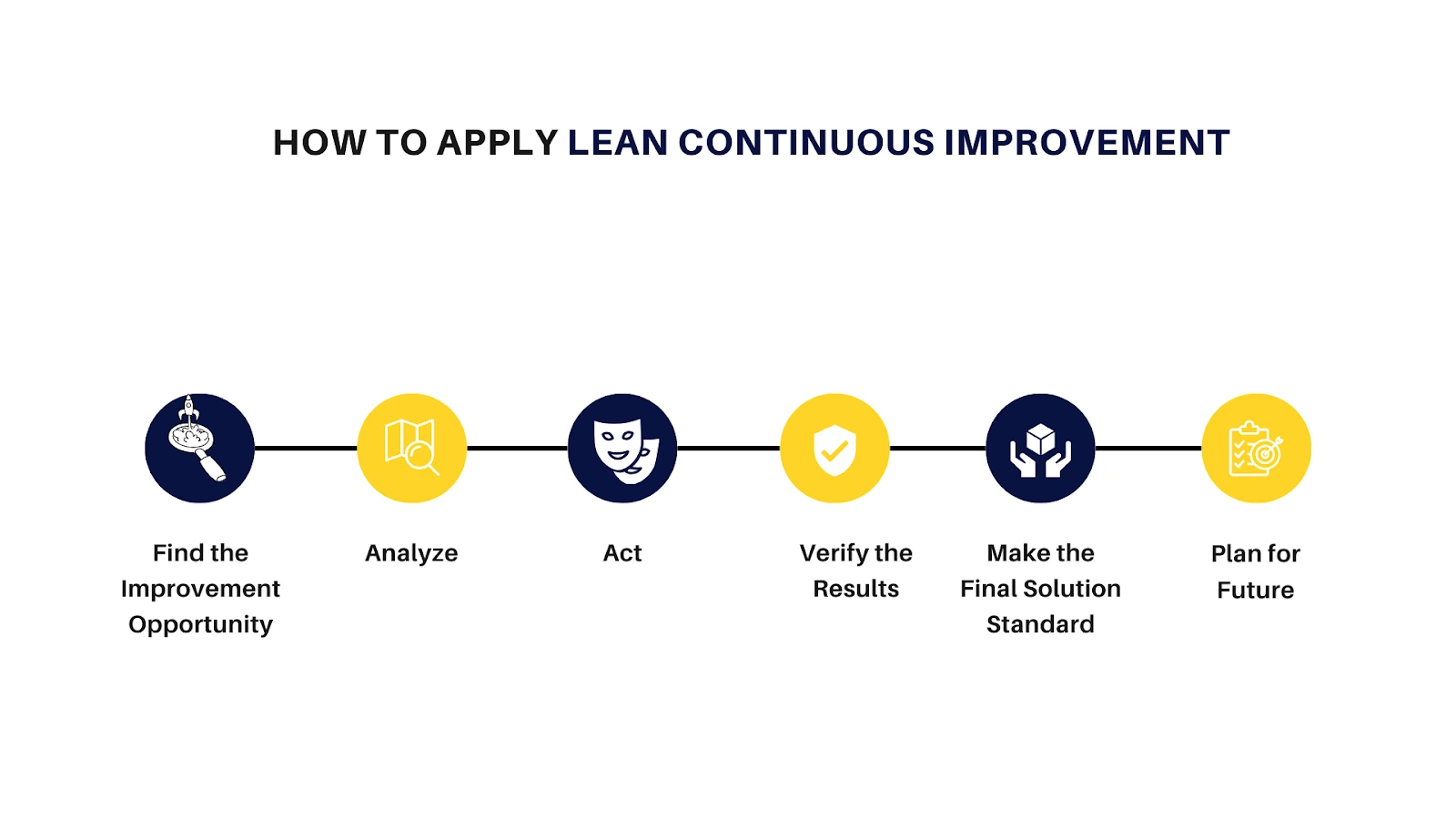
First, choose the right process to improve. Then, assess this process and pick a suitable challenge or problem to solve.
Next, find out the root cause of this challenge.
After analysis, make and execute a plan to fix these root causes.
Then, check the specific actions that will help you reach your goal.
Make sure to make the best solution standard so that you can keep the high level of performance.
Lastly, decide what to do with any remaining problems and measure how well your team did by setting an improvement target.
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is a four-step method for implementing and improving processes, products, and services. It is also known as the Shewhart cycle or the Deming cycle, after the two pioneers of quality management who popularized it. The PDCA cycle helps you to plan, test, evaluate, and refine your actions in a systematic and iterative way. It enables you to learn from your mistakes, adapt to changing conditions, and achieve your goals more effectively.The PDCA cycle consists of the following phases:
The PDCA cycle is not a one-time event, but a continuous process of improvement. By repeating the cycle, you can constantly monitor and improve your performance, and respond more quickly and effectively to customer needs and market changes. The PDCA cycle helps you to foster a culture of learning and innovation, and achieve excellence in your processes, products, and services.
Also Read:How to Improve Quality in Manufacturing?
Let’s review some of the top ten best continuous improvement tools and techniques.
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a powerful tool for continuous improvement that helps you to see and optimize the flow of value from the customer’s perspective. It allows you to visualize the entire process of creating and delivering a product or service, from the raw materials to the final delivery. By mapping the value stream, you can identify the sources of waste and inefficiency, and find opportunities for improvement.
The 5 Whys is a simple but effective technique for finding the root cause of a problem. It involves asking “why” repeatedly until you reach the underlying cause of the issue. The 5 Whys can help you to avoid superficial solutions and address the real problem.
Gemba Walks are a way of observing and improving the workplace by going to the place where the work is actually done. Gemba is a Japanese word that means “the real place”. Gemba Walks allow you to see the reality of the process, engage with the employees, and identify improvement opportunities.
A3 Problem-Solving is a structured and systematic approach to solving problems and implementing improvements. It uses an A3-size paper (11 x 17 inches) to document the problem, the analysis, the corrective actions, and the action plan. It also encourages clear communication and collaboration among the stakeholders involved in the problem-solving process.
Lean continuous improvement is not just a set of tools or techniques, but a mindset and a culture that can change your organization for the better. By embracing Lean principles, you can achieve amazing benefits that will make you and your customers happier, such as

Implementing lean continuous improvement systems in your manufacturing practices and at your vendor sites can have many benefits, such as:
How should you deploy continuous improvement and make your manufacturing operations Lean? This depends very much on the individual production situations and what performance outcomes you want to achieve. Sometimes, having third party manufacturing professionals (such as those at AMREP) evaluate the production situation can help to give additional insights into areas for improvement, and there are also manufacturing specialists who can provide technical leadership on lean manufacturing operations.
At AMREP, we take pride in our commitment to excellence through rigorous supplier and production audits By consistently creating the best solutions, we not only uphold the highest standards for our brand entity but also ensure that our customers receive products of unmatched quality. Trust AMREP for superior quality and unwavering dedication to delivering excellence in every solution we craft.
Read More : Performance Improvement Strategies in QA
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


05 - October 2023
05
October
2023
Layered Process Audit is a quality tool designed specifically for manufacturing management. It is meant for auditing organizational processes ...

21 - November 2023
21
November
2023
A process audit checklist is a tool that helps you to evaluate the performance and compliance of a process against a set of standards or criteria...

21 - November 2023
21
November
2023
VDA 6.3, an acronym for Verband der Automobilindustrie (German Association of the Automotive Industry), sets the stage for a meticulous examination ...
