Effective TQM Practices and Strategies for Business Success
Quality is a key differentiator for success, and organizations must adopt strategies that drive continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Total Quality Management...
By AMREP | Posted on January 07, 2025

The emphasis on customer satisfaction and continuous quality improvement is central to both quality assurance and quality control. Quality assurance focuses on processes and practices that provide confidence that the end result will be of high quality. Meanwhile, quality control measurements are the measurements or observations undertaken to objectively demonstrate that the quality management process has been fulfilled.
John Keenan Taylor, an environmental scientist known for his work in the field of quality assurance defines quality assurance as,
Quality Assurance refers to the proactive process of planning, defining, and managing quality standards throughout the production or service delivery process. QA focuses on preventing defects and ensuring the product or service meets predetermined quality criteria before it reaches the customer. It is a systematic approach to ensuring that quality is built into the product from the start.
The goal of QA is to prevent issues before they occur. By implementing best practices, standardized procedures, and regular audits, QA teams aim to create a work environment that fosters continuous improvement. QA is typically process-oriented and focuses on enhancing the entire workflow to achieve consistency and efficiency.
Quality management professionals Larry Webber and Michael Wallace define quality control as:
Quality Control , is a reactive process that focuses on identifying defects in the final product after it has been produced. QC ensures that the product meets the required quality standards and specifications by inspecting and testing it before it reaches the customer.
QC is typically product-oriented, where the focus is on detecting flaws and ensuring that the finished goods meet the desired specifications. It involves various techniques such as inspections, testing, and sampling to identify any defects in the product. QC aims to correct the issues found during inspection before the product is shipped to customers.
QA and QC share the common goal of improving product quality, but they differ in several critical aspects:
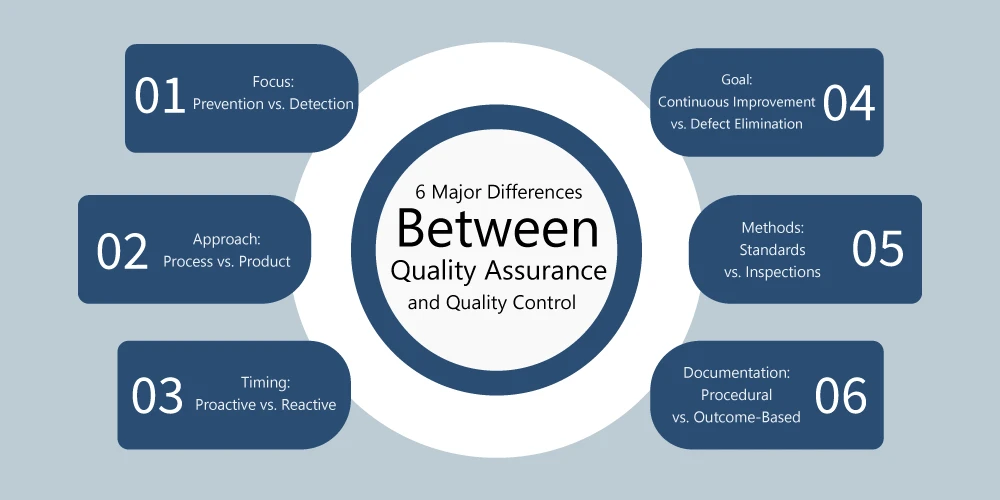
| QA focuses on preventing defects before they occur by improving processes, establishing standards, and ensuring compliance. | QC focuses on detecting defects after the product has been made, ensuring that any issues are identified and corrected. |
| QA is process-oriented, working to improve the entire production or service delivery process. | QC is product-oriented, concentrating on inspecting and testing the finished product. |
| QA is a proactive approach aimed at preventing problems from arising in the first place. | QC is a reactive approach, addressing problems only after they have been detected in the final product. |
| QA aims for continuous improvement in processes, reducing the likelihood of defects in future products. | QC aims to identify and eliminate defects in the current batch or final product before it reaches the customer. |
| QA uses methods like process mapping, training, and standard operating procedures to ensure quality standards are met. | QC uses methods like inspections, testing, and sampling to find defects in finished products. |
| QA involves extensive documentation to standardize processes, define quality standards, and track improvements. | QC focuses on documenting defects, corrective actions, and the outcomes of product inspections. |
Read More: Quality Engineering vs Quality Assurance: Understanding the Differences
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) both aim to ensure product quality but have distinct historical developments and approaches.
Quality Assurance (QA) originated in the early 20th century with the rise of systematic methods for improving processes. Pioneers like Walter Shewhart and W. Edwards Deming emphasized statistical methods and continuous improvement. QA evolved from manual inspection in the industrial era to include management principles, such as Total Quality Management (TQM), and standards like ISO 9000.
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, QA expanded to software development, with methodologies like Six Sigma, Agile, and DevOps revolutionizing the field. Automated testing and continuous improvement principles became central to modern QA practices.
Quality Control (QC), has its roots in the early days of manufacturing, with artisans personally monitoring product quality. During the Industrial Revolution, QC became more formalized with inspection systems in factories.
By the mid-20th century, statistical process control (SPC) and figures like Joseph Juran and W. Edwards Deming introduced data-driven methods to monitor and correct defects during production. QC is more focused on identifying and correcting defects in finished products or processes.
In recent years, Six Sigma, Lean manufacturing, and automation have transformed quality control. Digital tools and software-based QC enable faster, more efficient, and consistent quality management across manufacturing, software development, and services.
Handbook of Research on Technology Project Management, Planning, and Operations by Terry T defines SQA as:
Software Quality Assurance (SQA) is a set of activities and practices designed to ensure that software products meet specified requirements and are free of defects. It focuses on the entire software development process, from requirements gathering to design, coding, testing, and maintenance. The goal of SQA is to prevent software defects, improve development processes, and ensure that the final product is reliable, functional, and user-friendly.
SQA involves defining quality standards, setting up processes, and using tools to monitor and evaluate the development lifecycle. This includes test planning, code reviews, performance testing, and automated testing to identify and correct issues early. SQA helps teams deliver software that meets or exceeds user expectations and complies with industry standards.
Moreover, SQA is not limited to just testing; it also includes process improvements, documentation, training, and audits. These activities help maintain quality at every phase, ensuring that the software is scalable, secure, and performs as expected under various conditions. In essence, SQA is about building quality into the software from the very beginning, rather than just checking for it at the end.
An electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) bridges the gap between QA and QC by linking the preventive focus of QA with the detection and correction of QC. It ensures that the process improvements identified in QA are aligned with QC efforts to detect and fix defects. This smooth integration reduces errors, improves communication, and enhances overall product quality.
eQMS standardizes workflows, ensuring that every step in production follows best practices and meets quality standards.
eQMS manages documents, ensuring that only approved versions of procedures, work instructions, and policies are in use, preventing errors due to outdated or incorrect information.
eQMS provides automated audit trails, allowing traceability of process changes and ensuring continuous process improvement.
eQMS helps ensure compliance with regulatory requirements by tracking relevant standards and guidelines (e.g., ISO, FDA).
eQMS can track employee training and certifications, ensuring that staff is properly trained to follow QA processes.
eQMS captures defects in real-time during inspections and testing, ensuring that issues are recorded and addressed quickly.
eQMS helps manage non-conformances by providing tools for corrective actions, root cause analysis, and corrective action effectiveness.
eQMS can incorporate tools for statistical analysis, allowing data-driven decision-making for product quality improvements.
eQMS supports scheduling and tracking inspections, ensuring that QC tests are carried out consistently and results are recorded accurately.
eQMS generates reports on quality metrics and performance, providing valuable insights to improve the QC process.
Must see: The Importance of Quality Assurance in Quality Management
In some service organizations, the concept of quality control (QC) may not be immediately applicable, as there is no tangible product to inspect and manage. However, while the service itself may not be subject to QC in the traditional sense, the products involved in delivering the service—such as reports, contracts, designs, or even tangible items like rental cars or units of blood—may still require quality control. Ensuring the quality of these products is important. It helps meet customer expectations and maintain high service standards.
For example, a service organization that provides consulting services might not directly control the quality of the advice or consultation. However, it would still need to control the quality of documents produced, like reports or contracts. This ensures accuracy, clarity, and compliance with client requirements.
Similarly, organizations offering tangible services (e.g., car rentals or healthcare services) must ensure that the physical products involved meet defined quality standards before being provided to customers.
Inspection plays a crucial role in quality management for both products and services. It involves measuring, examining, and testing a product or service to ensure it meets specified requirements. This applies to both tangible products and services, where inspection helps identify deviations from quality standards, enabling corrective actions before final delivery.
Quality Assurance (QA) and auditing are closely linked in maintaining quality. Audits assess whether processes and outcomes align with established standards and requirements. They help identify gaps in the quality management system. Audits can be internal, compliance, product, or process-focused, with compliance audits verifying adherence to standards or regulations.
In summary, while QC may not always apply directly to services, the quality of any product involved in service delivery must be carefully managed. Inspection, QA, and auditing are essential to ensuring that processes, products, and services consistently meet customer requirements and regulatory standards.
At Amrep Inspect, we are committed to helping organizations implement effective QA and QC strategies, ensuring that quality is embedded at every stage of the process. With our innovative solutions and expertise, we empower businesses to maintain high quality standards, improve performance, and deliver exceptional results to their customers.Asmanufacturing experts, we provide the knowledge and tools necessary to optimize quality across all stages of production.
Read More : Defining Quality Control (QC) Processes
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


20 - December 2024
20
December
2024
Quality is a key differentiator for success, and organizations must adopt strategies that drive continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Total Quality Management...

20 - December 2024
20
December
2024
Organizations constantly strive to improve their processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve operational excellence. One philosophy that has stood the test...

10 - December 2024
10
December
2024
Quality Assurance Process Improvement focuses on identifying inefficiencies, eliminating bottlenecks, and implementing smarter strategies...
