What are Boeing’s recent quality problems?
On 24 August 2024, NASA announced that the astronauts Sunita Williams and Barry ‘Butch’ Wilmore would need to wait until next year to be safely returned to Earth. The astronauts were...
By AMREP | Posted on September 24, 2024

At the heart of societal growth and business success lies the fundamental element of trust. In the absence of trust, systems, relationships, and commercial endeavors crumble. For companies, gaining customer trust is not just important—it’s essential for survival.
Within the wide-ranging discipline of quality management, quality assurance (QA) plays an indispensable role, focused on elevating product standards and surpassing customer expectations. Through systematic implementation of processes and methodologies, QA aids organizations in boosting product reliability, mitigating compliance risks, and securing a competitive stance in the market. This proactive strategy not only aims to prevent defects and mistakes but also promotes an organizational culture geared towards constant enhancement and customer contentment.
This blog delves into the objectives, importance, and methods of quality assurance within the comprehensive scope of quality management.
Quality assurance refers to the systematic process used to ensure that a product or service adheres to specified criteria prior to its market release. Functioning as a preventive measure, QA is designed to refine development and testing processes, thereby preventing defects during product creation.
Quality assurance integrates several strategic roles within quality management systems:
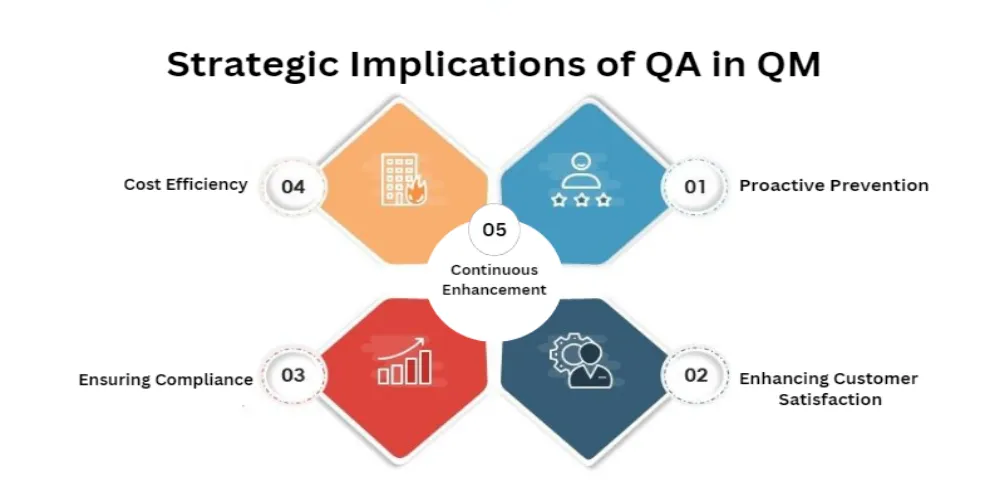
Proactive Prevention: QA identifies and rectifies potential problems before they transform into actual defects, a cost-saving measure compared to later-stage error detection.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction: By guaranteeing that the final product aligns with customer expectations, QA fosters customer loyalty and reinforces brand trust.
Ensuring Compliance: QA supports adherence to industry standards and regulatory demands, vital for sustaining market presence and avoiding legal repercussions.
Cost Efficiency: Early detection of defects through QA diminishes the expenses related to post-release fixes.
Encouraging Continuous Enhancement: QA advocates for ongoing improvements via feedback loops and iterative methods, boosting product quality and operational efficiency.
Quality assurance constitutes a fundamental element of thorough quality management frameworks like Total Quality Management (TQM) and the ISO 9001 standards. Integration occurs as follows:
Quality Planning: Initial quality planning defines product or service standards based on consumer needs and regulatory demands.
Quality Control and Testing: This phase involves continuous testing and quality control assessments to ensure outcomes meet preset standards, employing specific QA tools and methods.
Quality Improvement: Utilizing data from QA activities, processes are refined to enhance both efficiency and effectiveness, completing the quality management cycle.

Statistical Process Control (SPC): This technique employs statistical methods to oversee and control processes, optimizing performance.
Six Sigma: Focuses on enhancing process output quality by identifying and eliminating defect causes and minimizing variability.
ISO Certification: Adherence to ISO standards aids organizations in honing their QA processes and meeting international quality benchmarks.
Automated Testing Tools: In sectors like software development, these tools perform repetitive tasks and assess outcomes against expected results.
Reliability of Products: Consistent QA practices yield products that consistently meet or surpass customer expectations.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency: QA lessens the frequency of errors and defects, reducing waste and boosting production efficiency.
Competitive Advantage: Superior-quality products enhance brand reputation, giving firms an industry edge.
Resource Optimization: QA practices minimize errors and focus on continual improvement, optimizing resource use and enhancing operational efficiency.
While vital, implementing a robust QA system poses several challenges:
Upfront Costs: Initial establishment of QA processes can be costly, particularly for smaller firms.
Cultural Resistance: Embedding QA practices into an organizational culture can encounter resistance from employees accustomed to previous methods.
Technological Adaptability: Rapid technological advancements can render established QA processes outdated, necessitating regular updates and employee training.
For businesses like AMREP, maintaining customer trust through consistent quality assurance efforts is essential for continued success. By dedicating itself to rigorous QA practices, AMREP not only lays a solid trust foundation but also cements its status as a dependable industry leader. Moving forward, our unwavering commitment to excellence remains key to maintaining customer connections and securing a competitive market position.
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


10 - September 2024
10
September
2024
On 24 August 2024, NASA announced that the astronauts Sunita Williams and Barry ‘Butch’ Wilmore would need to wait until next year to be safely returned to Earth. The astronauts were...

09 - September 2024
09
September
2024
Maquiladoras are manufacturing facilities in Mexico that work together with a company’s main office in the United States. These plants let businesses take advantage...

16 - September 2024
16
September
2024
Mexico has always encouraged investors and foreign companies to manufacture in Mexico. This has been largely through tax incentives, grants, economic policies, duty...
