What is a Layered Process Audit?
Layered Process Audit is a quality tool designed specifically for manufacturing management. It is meant for auditing organizational processes ...
By AMREP | Posted on February 02, 2024
Six Sigma and Lean are two commonly used methods for improving manufacturing operational excellence. While both are process improvement methods, they have slightly different focus areas. Six Sigma in manufacturing aims to reduce variation to the point where defects are counted in the parts per million. Lean is more systems oriented - it looks at creating a production system that focuses on reducing waste, creating customer value, and creating continuous process improvement.
Six Sigma is critical for quality and precision in manufacturing. Originating in the 1980s at Motorola, it was a response to compete against Japanese manufacturing quality. The core of Six Sigma lies in its name and is derived from a statistical term signifying a near-perfect process with only 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
The heart of Six Sigma is its 5 phases, DMAIC: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Here’s what they mean -
As stated previously, Six Sigma is focused on eliminating variation. Variability in manufacturing can create manufacturing process problems which in turn leads to defects and production inconsistencies. The DMAIC methodology achieves variation elimination because it gets the manufacturer to scientifically and systematically do the following:
When properly deployed, Six Sigma can achieve reduced scrap, shorter cycle times, improved on-time delivery, reduced operating costs, and greater customer satisfaction.
Six Sigma is used widely across all manufacturing industries. Incidentally, it has also become a general business process improvement tool and is used in non-manufacturing industries as well.
Lean originated from the Toyota Production System in Japan post World War II. It's an approach targeted at maximizing value through eliminating waste in manufacturing operations.
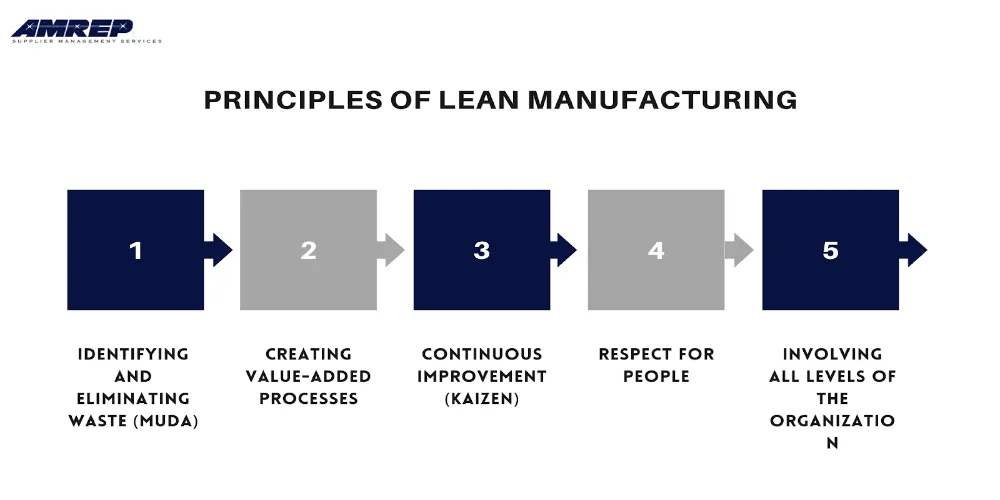
Lean's basis is built on numerous key principles:
To put into effect those principles, Lean makes use of several analytics tools:
When properly executed, Lean can result in greater manufacturing and business efficiencies.
Also, read about VDA 6.3 Process Audit
Here is a fuller comparison of Six Sigma and Lean.
Read about 5 Phases Of Six Sigma in detail.
During the 2000s, Lean and Six Sigma were integrated together to become a separate process improvement tool. This hybrid technique leverages Six Sigma’s statistics-driven defect elimination methods and Lean’s efficiency and waste reduction techniques. It results in a holistic and factual approach to improving performance by removing operational waste and preventing defect.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Six Sigma | Lean | Lean Six Sigma |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Reducing defects and variability | Eliminating waste | Combining defect reduction with waste elimination |
| Approach | Data-driven, statistical analysis | People-focused, respect for employees | Data-driven and people-focused |
| Core Principle | Process improvement through precision | Process simplification and efficiency | Comprehensive process improvement |
| Primary Application | Manufacturing (adaptable to other sectors) | Various industries including services and healthcare | Broad application across all sectors |
| Tools | DMAIC, DMADV | Kanban, Poka-yoke, VSM | Blend of Six Sigma and Lean tools |
Six Sigma and Lean are effective methodologies, each with particular strengths – Six Sigma's precise approach for decreasing defects and Lean's method for reducing waste. By integrating these strategies, Lean Six Sigma emerges as an ideal solution for improving manufacturing performance and reducing costs. This is particularly essential for businesses who are operating in increasingly complex business environments with rising cost pressures.
For companies with externalised production operations and vendor partners, it can be advantageous to deploy supplier development or manufacturing specialists from companies like AMREP at the production or vendor sites. They use their extensive experience in developing Lean Six Sigma initiatives for many manufacturing outfits to work on-site and improve production at your vendor sites. This results in lower costs and better production outcomes for all parties. To learn more, please don’t hesitate to contact us!
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


05 - October 2023
05
October
2023
Layered Process Audit is a quality tool designed specifically for manufacturing management. It is meant for auditing organizational processes ...

21 - November 2023
21
November
2023
A process audit checklist is a tool that helps you to evaluate the performance and compliance of a process against a set of standards or criteria...

21 - November 2023
21
November
2023
VDA 6.3, an acronym for Verband der Automobilindustrie (German Association of the Automotive Industry), sets the stage for a meticulous examination ...
