Effective TQM Practices and Strategies for Business Success
Quality is a key differentiator for success, and organizations must adopt strategies that drive continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Total Quality Management...
By AMREP | Posted on June 02, 2025
In any business that depends on external suppliers, quality and consistency are non-negotiable. But how can you be sure that your suppliers are truly delivering what they promise? One of the most effective tools businesses use to know this is the supplier audit.
This comprehensive guide will explore the concept, purpose, types, process, benefits, and best practices of supplier audits.

A supplier audit is a systematic and independent evaluation of a supplier’s processes, systems, and operations to verify their ability to meet the requirements of their customers, regulatory standards, and contractual agreements. It involves a detailed examination of the supplier’s manufacturing practices, quality control measures, safety protocols, compliance with legal and environmental standards, and overall operational efficiency.
Supplier audits are often conducted by the purchasing company, third-party auditors, or regulatory bodies to ensure that the supplier maintains the agreed-upon quality, delivery schedules, and ethical standards.
The purpose of supplier audits is to:
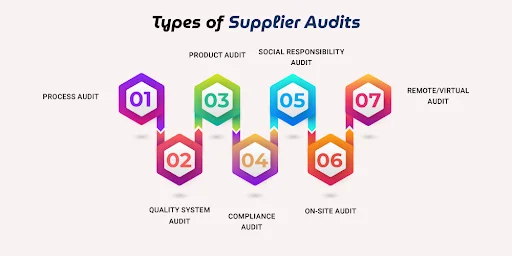
Supplier audits come in various forms depending on the objectives, scope, and focus areas:
A process audit focuses on examining the supplier’s production and operational workflows. The goal is to verify that these processes are not only efficient but also standardized and consistently followed. Auditors evaluate how well the supplier implements quality management practices during production, including controls, documentation, and process performance. This type of audit helps identify inefficiencies or deviations that could affect product quality or delivery timelines, ensuring processes are optimized and repeatable.
The quality system audit assesses the supplier’s overall Quality Management System (QMS). This audit often involves benchmarking against recognized standards such as ISO 9001. Auditors review policies, procedures, records, and documentation to determine if the supplier maintains consistent quality controls throughout their operations. The audit verifies that the QMS effectively supports product quality, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement efforts.
A product audit involves direct inspection and testing of specific products or batches supplied. The objective is to confirm that the items meet the agreed-upon specifications, quality standards, and functional requirements. This audit often includes physical examination, measurement, and performance testing. Product audits are essential for detecting defects, verifying compliance, and ensuring that what is delivered matches what was promised.
Compliance audits focus on ensuring that suppliers adhere to applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards. This includes environmental regulations, safety requirements, labor laws, and ethical guidelines. Auditors check documentation and on-site practices to verify conformity with legal and regulatory obligations. Compliance audits help reduce risks related to legal penalties, environmental harm, and reputational damage.
This audit evaluates a supplier’s practices concerning social responsibility, including labor conditions, human rights, workplace safety, and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. Auditors assess factors such as fair wages, working hours, child labor policies, and employee welfare. This type of audit is increasingly important for companies committed to ethical sourcing and sustainable supply chains, ensuring suppliers operate responsibly and ethically.
An on-site audit involves auditors physically visiting the supplier’s facilities. This allows a hands-on review of production processes, quality controls, safety measures, and staff interviews. On-site audits provide a comprehensive, real-time understanding of how the supplier operates. Auditors can observe workflows, verify documentation, and directly interact with personnel to clarify issues or gather insights.
Remote or virtual audits are conducted online using video conferencing tools, digital document sharing, and other technologies. This method is especially useful when travel is limited or cost-prohibitive. Although auditors cannot physically inspect facilities, they can review records, observe processes via video, and interview key staff remotely. Remote audits offer flexibility and efficiency while maintaining oversight of supplier performance.
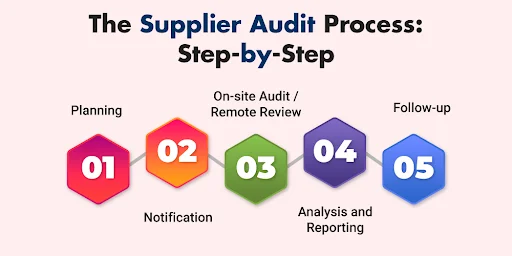
Conducting a thorough supplier audit involves multiple stages:
Conducting supplier audits brings a host of benefits that protect your business, enhance product quality, and foster long-term partnerships. Let’s explore why these audits are so crucial and the advantages they offer.
A supplier audit ensures that the products meet quality standards consistently, reducing defects and customer complaints.
Audits help identify potential risks early such as production delays, non-compliance issues, or financial instability.
Regular audits help maintain adherence to regulatory, safety, and environmental standards, avoiding legal penalties.
Audits motivate suppliers to adopt best practices, streamline processes, and improve efficiency.
By preventing defects and reducing rework, supplier audits help save costs related to quality failures and supply disruptions.
Regular audits foster open communication and strengthen trust between buyers and suppliers.
Audits verify ethical labor practices and environmental responsibility, aligning the supply chain with corporate values.
To get the most out of your supplier audits, it’s essential to approach them with a clear strategy and proven methods. Implementing best practices ensures audits are thorough, objective, and lead to meaningful improvements in your supply chain. Below are key practices to follow for conducting effective supplier audits:
Before starting an audit, establish well-defined criteria based on industry standards, regulatory requirements, and your specific contract terms. These benchmarks guide the audit process and help focus on critical areas such as quality management systems, production processes, safety protocols, and compliance. Clear criteria ensure consistency across audits and make it easier to measure supplier performance objectively.
An effective audit depends largely on the skills and knowledge of your auditors. Provide comprehensive training so that your audit team understands relevant technical aspects, quality standards, and auditing techniques. Skilled auditors are better equipped to identify issues, ask the right questions, and interpret findings accurately, which leads to more reliable and actionable audit results.
Supplier audits should be impartial assessments based on evidence, not assumptions or personal opinions. Auditors must remain neutral throughout the process, focusing on documented facts such as process records, certifications, and direct observations. Objectivity builds trust with suppliers and ensures that audit outcomes are credible and defensible.
Rather than treating audits as a one-sided inspection, approach them as a collaborative effort with your suppliers. Open communication during the audit helps identify root causes of problems and fosters a constructive environment for problem-solving. Encouraging supplier participation promotes transparency, improves relationships, and increases the likelihood that corrective actions will be accepted and implemented effectively.
Thorough documentation is crucial for tracking audit findings and progress. Record all observations, non-conformities, and best practices in detail. Keep copies of supporting evidence like photographs, checklists, and interview notes. Well-maintained records provide a clear audit trail, assist in follow-up activities, and serve as a reference for future audits or compliance verification.
An audit is not complete once the report is delivered. Follow up with the supplier to ensure corrective actions are implemented within agreed timelines. Monitoring progress and verifying improvements prevent recurring issues and demonstrate your commitment to continuous quality enhancement. If necessary, schedule follow-up audits to confirm sustained compliance and performance.
Leverage modern digital tools to streamline the audit process. Audit management software can simplify checklist creation, data collection, and reporting. Virtual audit technologies enable remote assessments through video conferencing and digital document sharing, making audits more flexible and efficient. Utilizing technology helps reduce human error, save time, and improve communication between your team and suppliers.
Supplier audits are a vital tool for businesses to maintain a reliable, high-quality, and compliant supply chain. They help reduce risks, improve product quality, and build stronger partnerships. Whether you are a manufacturing company, retailer, or service provider, conducting regular supplier audits can save you time, money, and reputational damage in the long run.
Investing in supplier audits means investing in the sustainability and success of your entire supply chain. With a well-planned and executed supplier audit program, you can confidently ensure that your suppliers align with your business goals and deliver value consistently.
At AMREP Inspect, we understand that supplier audits are more than just a checklist—they are a critical investment in your business’s quality, compliance, and long-term success. Partner with us to implement thorough and effective supplier audit programs that protect your supply chain and drive continuous improvement. Together, we’ll help you build stronger supplier relationships and ensure consistent value delivery every step of the way.
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


20 - December 2024
20
December
2024
Quality is a key differentiator for success, and organizations must adopt strategies that drive continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Total Quality Management...

20 - December 2024
20
December
2024
Organizations constantly strive to improve their processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve operational excellence. One philosophy that has stood the test...

10 - December 2024
10
December
2024
Quality Assurance Process Improvement focuses on identifying inefficiencies, eliminating bottlenecks, and implementing smarter strategies...
