Guide to Qualifying New Suppliers in Malaysia for Manufacturing Success
Malaysia is a premier manufacturing hub in Southeast Asia. According to the Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA), “Malaysia, with its extensive trade....
By AMREP | Posted on August 26, 2025
Electrostatic discharge, or ESD, is the sudden flow of electricity between two charged objects. It happens instantly and often without any visible sign, causing severe damage to delicate electronic products.
For example, the slight shock you feel when you touch a doorknob after walking across a carpet. In daily life, it is just a quick zap. Inside an electronic device, the same spark can silently destroy a chip or weaken a circuit. The damage may show up right away or months later.
However, following best practices like grounding yourself, using protective packaging, and working in a controlled environment can significantly reduce the risk of ESD damage. With consistent habits and controls, you can protect your products, reduce costly failures, and keep your customers' trust. This guide will walk you through the risks, common causes, and proven strategies to keep ESD from harming your electronic products.
Microchips and circuit boards are incredibly delicate. They are designed to handle only tiny amounts of electricity. When a discharge hits, it can burn tiny pathways, weaken joints, or break down protective layers. Sometimes the device stops working immediately. Other times, the damage is hidden and shows up later, causing unpredictable failures. ESD can damage an electronic product in different ways, as described below.
Sometimes ESD damage shows up right away. A single spark can severely damage a chip or circuit, rendering the product unusable. In most cases, the device is beyond repair.
In many situations, the damage isn't visible at first. The product may seem fine when it leaves the factory, but the weakened part eventually breaks down. Such a hidden failure is often the most frustrating because it causes problems weeks or months later, usually after the customer has already started using the product.
ESD can also weaken a product without stopping it completely. The device still works, but its performance slowly drops. It may become less reliable, lose efficiency, or behave in unexpected ways over time.
ESD can affect various industries. For example, Phone chips may fail after a short period of use. Semiconductor wafers can be ruined during production. Even medical devices can stop working when reliability is most critical. All of these problems begin with a spark that is too small for the human eye to see.
The result is often reduced reliability and costly product returns. For businesses, it can mean higher warranty expenses and frustrated customers who lose confidence in the brand.

One of the most significant sources of static electricity is the human body. Simply walking across a floor or touching a chair can build up a charge. When that charge is released into a circuit or chip, it can cause severe damage.
Everyday materials like plastic packaging, clothing, or even a work surface can create static through friction. When parts come into contact with these materials, the risk of discharge increases.
Dry air makes static buildup worse. In facilities where humidity is too low, charges form more easily and stay on surfaces longer, making electronics more vulnerable.
If workers handle parts without grounding themselves, ESD is likely to occur. A simple touch is enough to pass along a harmful charge to a sensitive component.
Storing or shipping components in regular plastic bags or foam can also lead to problems. Without protective packaging, static charge can collect on products during storage or transport and discharge when they are handled, often causing damage.
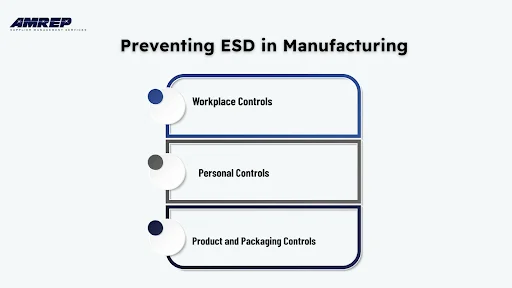
The work environment is the first line of defence against static discharge. A well-prepared facility reduces the chances of charges building up and harming sensitive parts.
Since people are the most common source of static, personal protection is essential. With the right equipment and training, workers can safely handle even the most delicate components.
Protecting parts doesn't stop at the workstation. Proper storage and packaging keep products safe while they move through the supply chain.
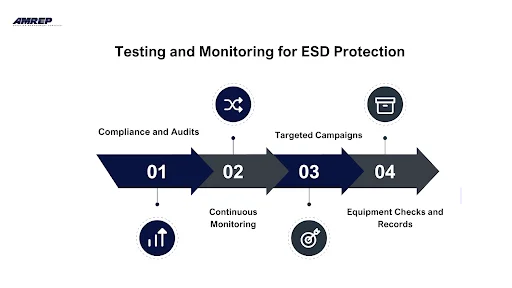
Even the best ESD controls only work if they are tested and monitored regularly. Continuous checks ensure that protective measures stay effective and meet industry standards.
Regular audits help confirm that ESD practices follow international guidelines and keep operations consistent.
Workstations and operators should be monitored in real time to prevent lapses in protection.
Regular testing of tools and equipment ensures long-term reliability and prevents unnoticed failures.
Preventing ESD is not only about safe handling. Good design choices can make products more resilient to static discharge from the very beginning. By adding protection in the design stage, manufacturers reduce failures and improve long-term reliability.
Small components can act as shields against sudden surges of electricity.
The way a circuit board is designed also affects its resistance to ESD.
Stronger ESD protection often incurs additional costs, but it pays off by reducing failures.
Strong ESD protection is not only about safeguarding electronics. It also brings clear business advantages that directly affect profits and reputation.
When products are protected from ESD, they last longer and perform as expected.
Every failure has a price. Preventing ESD helps keep those costs under control.
A reliable product builds trust and credibility in the market.
International markets often require proof of compliance with ESD standards.
Must check out our blog on QC Tests and Checks in Quality Management for a better understanding.
Preventing ESD doesn't have to be complicated. Following a few consistent habits makes a big difference in keeping products safe and reliable.
Electrostatic discharge may be invisible, but its effects on electronics are very real. A single spark can damage delicate components, shorten product life, and lead to costly failures. However, the ESD damage can be prevented by the correct workplace setup, proper handling, safe packaging, and innovative design strategies. ESD control protects more than electronics by keeping your products reliable, your customers happy, and your brand reputation strong.
At AMREP, with our expert electronics quality engineering services and solutions, you can save costs, improve reliability, and deliver products that stand the test of time.
Need expert guidance on building a safer, more reliable process? Reach out today and take the first step toward complete ESD control.
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


12 - May 2025
12
May
2025
Malaysia is a premier manufacturing hub in Southeast Asia. According to the Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA), “Malaysia, with its extensive trade....

22 - April 2025
22
April
2025
Healthcare is rapidly evolving, ensuring consistent and high-quality patient care. Total Quality Management (TQM) in healthcare is more than just a buzzword—it is a powerful....

16 - April 2025
16
April
2025
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a mindset that involves everyone in the organization working toward a common goal: achieving excellence through quality. From....
