Choosing the Best QA Management Partner: Trends and Services
In today's competitive markets quality assurance (QA) management is essential for businesses aiming to meet and exceed the strict standards of product quality...
By AMREP | Posted on September 25, 2024
QA systems focus on monitoring and improving every stage of development to prevent issues before they occur.
The concept of quality assurance dates back to the early 20th century, with pioneers like Frederick Winslow Taylor and his principles of scientific management, which emphasized efficiency and consistency in production. Later, during World War II, statistical quality control became more widespread, and the need for standardized processes grew, giving rise to more formal QA systems in manufacturing.
This blog covers the fundamentals of Quality Assurance (QA) systems, their importance for businesses, approaches to implementation, key processes, industry examples, and the role of QMS software in enhancing QA systems.
A Quality Assurance (QA) system is a formalized framework designed to ensure products or services meet established quality standards. It involves a series of policies, processes, and procedures aimed at preventing defects and maintaining consistency across production or service delivery. This system involves both proactive and reactive measures, such as audits, process checks, and feedback loops, to maintain consistent quality.
A QA system is important for businesses because it helps avoid costly mistakes, reduces defects, and ensures customer satisfaction. By implementing a QA system, businesses can monitor the entire production cycle, identify potential issues before they arise, and continually improve processes. Moreover, a strong QA system boosts a company’s reputation, ensuring compliance with industry standards and helping secure certifications like ISO.
There are several approaches to implementing QA, each with a focus on different methodologies:
Process-Oriented Approach: Focuses on monitoring the processes used to create products and services.
Standards-Based Approach: Ensures that quality processes comply with specific standards like ISO 9001 or Six Sigma.
Risk-Based Approach: Prioritizes identifying and managing risks that could affect product quality.
Continuous Improvement: Emphasizes ongoing enhancements to processes, using feedback and analysis to prevent future issues.
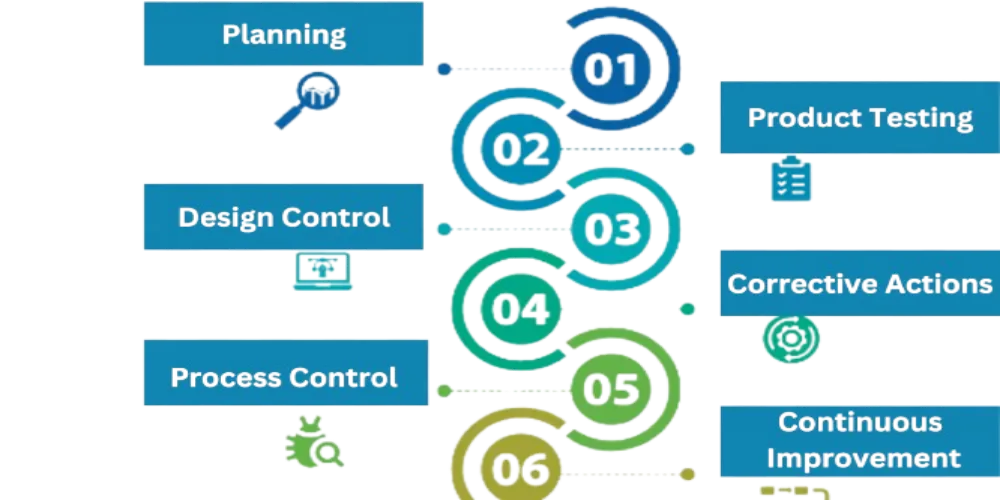
The processes of a QA system are designed to ensure that quality is maintained throughout production:
QA is implemented across a wide range of industries. Some examples include:
An effective QA system provides several benefits, including:
Quality Assurance is focused on the processes used to create the product, ensuring that everything is done correctly from the start. Quality Control, on the other hand, is concerned with inspecting the final product to catch any defects. QA is proactive, while QC is reactive.
| Aspect | Quality Assurance (QA) | Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive process to prevent defects | Reactive process to identify defects |
| Focus | Process improvement | Product inspection |
| Timing | Throughout the production process | After the product is made |
| Responsibility | Shared across teams | Specific QC personnel |
| Objective | Prevent defects and improve processes | Detect defects in finished products |
| Methods | Process audits, planning, training | Inspections, testing, sampling |
The primary difference between QA and QC lies in their focus. QA is about ensuring the processes lead to quality outcomes, while QC is focused on inspecting the final product to detect defects. In practical terms, QA ensures that processes are optimized and continuously improved, while QC tests the final product to make sure it meets standards before reaching the customer.
| Aspect | Quality Assurance (QA) | Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|
| Application Focus | Applied throughout the entire production process to prevent defects | Applied to the final product to identify defects |
| Timing | Implemented during planning, design, and production stages | Applied after production or at critical checkpoints |
| Responsibility | Shared across all teams, including management and staff | Specific quality control personnel, inspectors, or testers |
| Proactive vs. Reactive | Proactive approach, preventing issues before they occur | Reactive approach, identifying and fixing issues after they occur |
| Nature of Application | Focuses on improving processes and ensuring quality standards are followed | Focuses on inspecting the product to ensure it meets specifications |
| Methods | Process audits, quality planning, training, continuous improvement | Sampling, performance testing, inspections, defect correction |
Quality Management System (QMS) software plays a vital role in supporting and streamlining Quality Assurance (QA) processes within an organization. By automating various aspects of QA, QMS software ensures consistency, efficiency, and compliance across the board. Here’s how QMS software enhances QA systems:
QMS software provides a centralized platform for managing all quality-related documents, such as standard operating procedures (SOPs), quality manuals, policies, and audit reports. This centralized control ensures that all team members have access to the latest version of documents, reducing errors due to outdated information.
QMS software automates the process of conducting internal and external audits, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations like ISO 9001. It tracks and schedules audits, generates reports, and highlights areas that need improvement. This makes it easier to maintain compliance without manual oversight.
One of the biggest advantages of QMS software is its ability to provide real-time data on quality metrics. It enables businesses to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track defects, and measure process efficiency. Real-time reporting helps management make informed decisions to improve quality processes.
QMS software makes it easier to implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) by automating the identification and resolution of issues. When a defect or deviation is identified, the system tracks the issue, assigns responsibilities, and ensures timely resolution to prevent future problems.
Quality Assurance (QA) system is essential for any business looking to maintain high standards and ensure consistent product or service quality. By focusing on key processes like planning, design control, and continuous improvement, businesses can prevent defects, boost customer satisfaction, and ensure compliance with industry standards. At AMREP, we understand the value of quality and are committed to helping you implement effective QA systems that drive success in your operations. Reach out to us today to elevate your quality management processes.
Read More :
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


25 - September 2024
25
September
2024
In today's competitive markets quality assurance (QA) management is essential for businesses aiming to meet and exceed the strict standards of product quality...

24 - September 2024
24
September
2024
At the heart of societal growth and business success lies the fundamental element of trust. In the absence of trust, systems, relationships, and commercial endeavors...

16 - September 2024
16
September
2024
Mexico has always encouraged investors and foreign companies to manufacture in Mexico. This has been largely through tax incentives, grants, economic policies, duty...
