What is a Layered Process Audit?
Layered Process Audit is a quality tool designed specifically for manufacturing management. It is meant for auditing organizational processes ...
By AMREP | Posted on December 30, 2023
One of the key tools AMREP uses in its quality engineering work is the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP). Here, we explain what it is and how it is used.
Originating in the automotive industry, the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) has become a backbone in ensuring safety and reliability. In fact, a survey by the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) revealed that 90% of automotive suppliers have incorporated PPAP as a crucial aspect of their quality management systems, underscoring its widespread adoption and impact.
PPAP isn't confined to a specific industry or geographical location. The International Automotive Task Force (IATF) has established PPAP as a global standard, thus ensuring that the principles of quality assurance are universally applied.
In this blog, we will explain the fundamental aspects of PPAP, including its objectives, its execution, the governing standard that ensures its uniform application, and its benefits for industries.
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is a standardized process used in various industries, particularly automotive and aerospace, to ensure that suppliers can consistently produce parts that meet customer requirements. It provides a framework for suppliers to demonstrate their understanding of customer specifications and their ability to manufacture high-quality products.
The purpose of PPAP is clear to prevent defects and errors from creeping into the manufacturing process. It's about catching problems early on, when they're still manageable, rather than discovering them later, when they can cause costly delays and reputational damage.
The objectives of PPAP are diverse. It aims to:
The PPAP is used in the manufacturing processes to ensure that the parts that reach the assembly line are not just components but building blocks of quality and excellence.
PPAP involves a series of steps that verify the supplier's understanding of design specifications, the capability of their manufacturing process, and the quality of the produced parts.
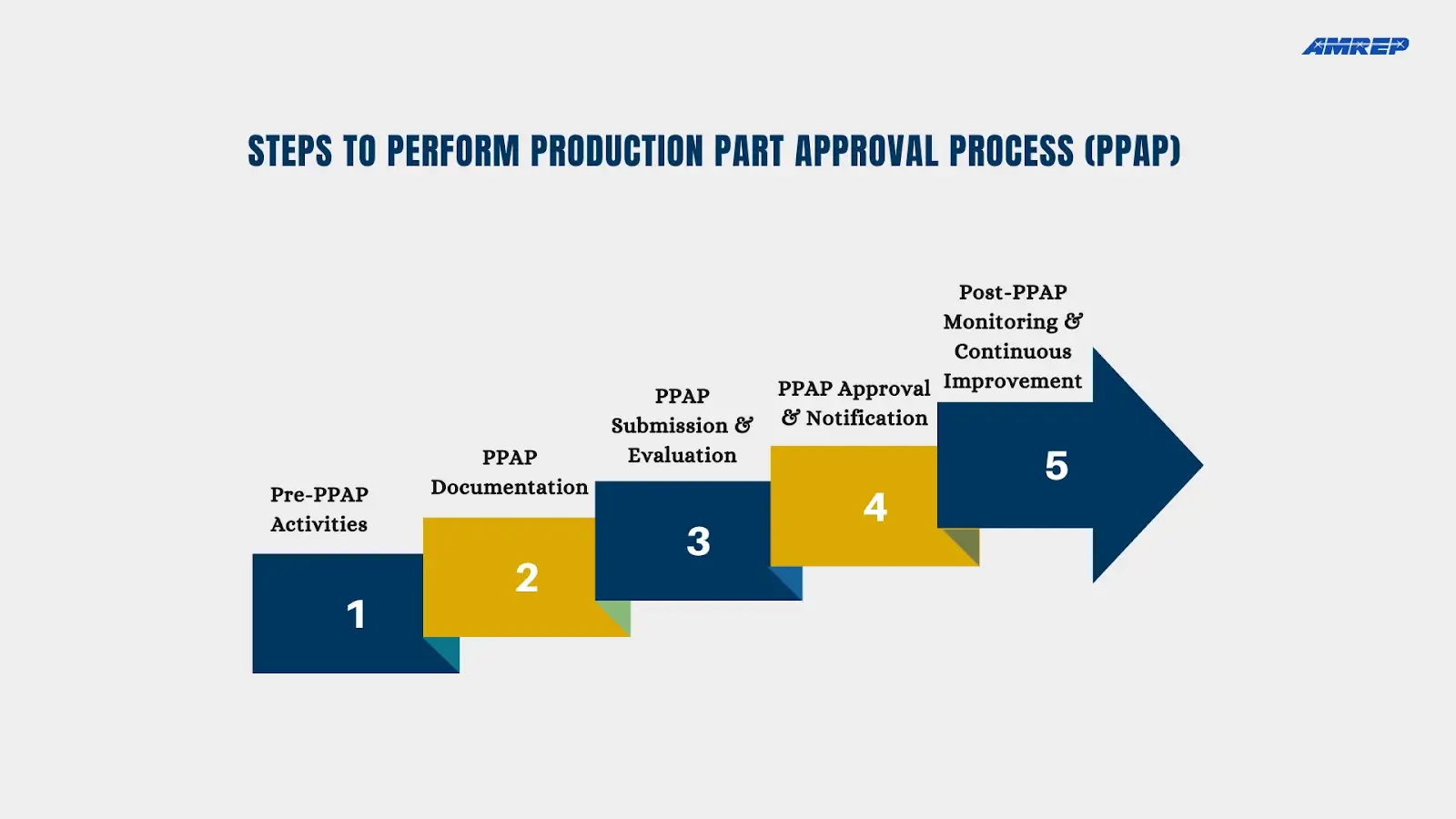
Before embarking on the production journey, it's crucial to establish clear and effective communication channels between the supplier and the customer. This open dialogue fosters mutual understanding and ensures that both parties are aligned on expectations and deliverables. Regular meetings, email correspondence, and a dedicated project management platform can effectively facilitate this exchange of information.
Design reviews are essential checkpoints in the pre-PPAP phase, ensuring that the supplier's interpretation of the customer's specifications is accurate and complete. These reviews involve a thorough examination of design documents, drawings, and prototypes to identify any potential discrepancies or areas of ambiguity. Through collaborative discussions, both parties can refine the design to meet the customer's exact requirements.
Control plans and process flow diagrams are the roadmaps that guide the manufacturing process. Control plans outline the specific measures and procedures in place to ensure product quality and consistency, while process flow diagrams provide a visual representation of the production steps involved. These documents serve as valuable tools for identifying and preventing potential defects, ensuring that the supplier delivers products that meet the customer's expectations.
The PPAP Submission Warrant (PSW) is the official document that formally initiates the PPAP process. It serves as a comprehensive summary of the PPAP submission, providing the customer with an overview of the supplier's readiness for production. The PSW typically includes the following information:
In addition to the PSW, the PPAP submission package includes a collection of relevant documents that demonstrate the supplier's ability to meet the customer's requirements. These documents typically fall into the following categories:
These documents provide detailed information about the design of the part, including drawings, specifications, and any engineering change notices (ECNs) that have been issued.
The PFMEA is a tool used to identify and prioritize potential failure modes in the manufacturing process. It includes a description of each failure mode, its potential effects, and the preventive controls in place to mitigate the risk of occurrence.
MSA studies are conducted to ensure that the measuring instruments used to inspect the part are capable of making accurate and consistent measurements.
These documents provide evidence that the part meets the customer's dimensional requirements and that the materials used to make the part meet the specified performance standards.
The AAR documents any appearance defects that have been identified on the part and includes a plan for addressing them.
The PPAP submission typically includes a sample of production parts and a master sample. The master sample is a reference part that represents the ideal quality level for the production parts.
Checking aids are the tools used to inspect the part. Records of compliance with customer requirements demonstrate that the supplier has met all of the customer's specific requirements.
Once all of the relevant documents have been collected, they should be organized in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for the customer to review. The PPAP submission package should be submitted to the customer in a timely manner, allowing ample time for review and approval.
Once the supplier has diligently compiled the PPAP documentation, the next crucial step is to submit the PPAP package to the customer for review and evaluation. This formal handover marks a significant milestone in the production process, signaling the supplier's readiness to commence mass production.
PPAP submissions have different levels.The level of PPAP submission (given in table below) that is required will depend on the customer's specific requirements. In general, higher levels of PPAP submission are required for more critical parts or parts that are manufactured to tighter tolerances.
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Part Submission Warrant* (PSW) only |
| 2 | PSW with product samples and limited supporting data |
| 3 | PSW with product samples and complete supporting data |
| 4 | PSW and other requirements as defined by the customer |
| 5 | PSW with product samples and complete supporting data available for review at the supplier's manufacturing location |
*Part Submission Warrant (PSW) is the most basic level of PPAP submission. It involves submitting only the PSW, which is a document that summarizes the key information about the part, such as the part number, revision level, and customer requirements.
The customer plays a pivotal role in ensuring the highest quality standards. Upon receiving the PPAP package, the customer meticulously examines the documentation and samples to verify that the supplier has effectively implemented all the necessary measures to produce parts that meet the specified requirements. This thorough evaluation involves scrutinizing design documents, process flow diagrams, test results, and sample parts to ensure that no detail is overlooked.
Throughout the evaluation process, the customer may encounter instances that require further clarification. In such cases, the customer engages in open communication with the supplier, seeking additional information or explanation to fully comprehend the supplier's approach and address any potential discrepancies. This collaborative dialogue fosters a shared understanding and ensures that both parties are aligned on expectations.
Following a comprehensive evaluation of the PPAP package, the customer issues a formal decision regarding PPAP approval. If the customer is satisfied that the supplier has demonstrated the ability to consistently produce parts that meet all specified requirements, the customer grants PPAP approval. This approval signifies a green light for the supplier to commence mass production of the part.
In instances where the customer identifies areas that require improvement, the customer requests corrective actions from the supplier. The supplier diligently addresses the identified issues, implementing appropriate measures to rectify any discrepancies and enhance overall quality.
Upon the supplier's successful implementation of corrective actions and resubmission of the PPAP package, the customer conducts a final review. If the customer is satisfied with the supplier's efforts and confirms that all requirements have been met, the customer grants final PPAP approval. This final approval marks the culmination of the PPAP process, signifying a successful collaboration between supplier and customer in achieving the highest quality standards.
Even after the formal PPAP process is complete, the relationship between supplier and customer remains dynamic and ever-evolving. Establishing ongoing communication and collaboration is essential for maintaining the high quality standards achieved during the PPAP phase. Regular meetings, data sharing, and joint problem-solving sessions foster a spirit of continuous improvement and ensure that both parties remain aligned on expectations and objectives.
The quest for excellence extends beyond the initial PPAP approval. Close monitoring of the production process and product quality is paramount to ensuring consistency and identifying any potential deviations from the established standards. This vigilant oversight involves regular inspections, data analysis, and feedback loops that enable timely corrective actions and prevent defects from reaching the customer.
The spirit of continuous improvement is the cornerstone of long-term success. By actively seeking out opportunities for betterment, both the supplier and the customer can elevate product quality and process efficiency to new heights. This pursuit of excellence may involve implementing innovative technologies, refining manufacturing techniques, or adopting best practices from industry leaders.
Through ongoing collaboration, vigilant monitoring, and a relentless pursuit of improvement, the supplier and customer can forge a lasting partnership that delivers exceptional products and fosters mutual success.
Read More: What is a Manufacturing Process Audit?
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is primarily governed by the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG), an association of automakers, suppliers, and service providers. The AIAG publishes the PPAP manual, which provides detailed guidelines for the PPAP process. The manual is updated periodically to reflect the latest industry best practices.
In addition to the AIAG, individual original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) may also have their own PPAP requirements. These requirements may be more stringent than the general AIAG guidelines. Suppliers should always consult with their customers to determine the specific PPAP requirements that they must meet.
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) offers a multitude of benefits that enhance quality, streamline operations, and strengthen supplier-customer relationships. Here are some of the key advantages of implementing PPAP:

The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is a multifaceted process that meticulously examines every aspect of production, from design specifications to manufacturing procedures, ensuring that every part meets the highest standards. In essence, PPAP is not merely a process; it is a philosophy, a commitment to excellence that pervades every aspect of manufacturing.
At AMREP, our quality engineers provide additional technical support and leadership to the supplier’s PPAP process. Having a third party monitor the PPAP process and independently review the documentation, data collection and analysis, materials, processes and product samples, can help enhance the PPAP outcomes. A third party can also ensure that the PPAP procedures are correctly carried out and that no critical steps are missed. Many automotive companies use third party companies as an independent party to cross-validate the supplier’s PPAP process.
By integrating Production Management Solutions, AMREP not only reinforces the effectiveness of the PPAP process but also brings a more systematic, data-driven approach to quality assurance in supplier management.
Read More : How AMREP Inspect Supports Efficient Production Setup
Contact Us To See What We Can Do
Call Us
Mon - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed


05 - October 2023
05
October
2023
Layered Process Audit is a quality tool designed specifically for manufacturing management. It is meant for auditing organizational processes ...

21 - November 2023
21
November
2023
A process audit checklist is a tool that helps you to evaluate the performance and compliance of a process against a set of standards or criteria...

21 - November 2023
21
November
2023
VDA 6.3, an acronym for Verband der Automobilindustrie (German Association of the Automotive Industry), sets the stage for a meticulous examination ...
